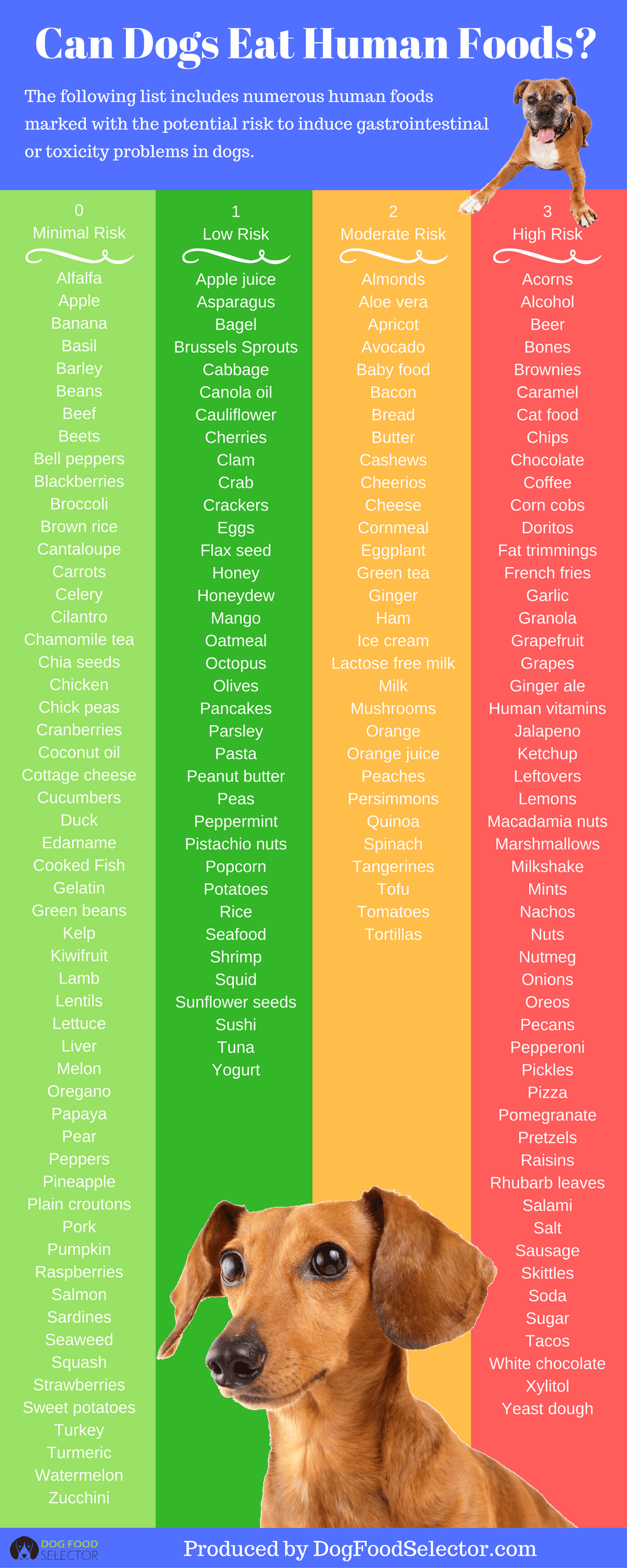
As a responsible dog owner, you’re always looking for ways to enhance your furry friend’s well-being. While a balanced diet of commercial dog food is crucial, many common human foods can also be offered as healthy and delicious treats. Understanding which of these are safe is key to avoiding potential health risks. This guide explores a variety of human foods that can be safely incorporated into your dog’s diet, offering nutritional benefits and a welcome change from their usual kibble.
Safe Human Foods for Canine Companions
Many everyday foods enjoyed by humans can also be part of a dog’s diet, provided they are prepared correctly and offered in moderation. These options can offer valuable nutrients and make for enjoyable occasional treats.
Grains and Starches
- Bread: Small amounts of plain bread, without any added spices or harmful ingredients like raisins, can be given to dogs. However, it offers minimal nutritional value and is primarily a source of carbohydrates and calories. Opt for homemade versions over store-bought to avoid preservatives.
- Corn: A common ingredient in many dog foods, corn is generally safe. However, ensure your dog does not consume the cob, as it can cause digestive issues or blockages.
- Popcorn: Plain, air-popped popcorn (unsalted and without butter) can be a safe treat. It contains riboflavin and thiamine, beneficial for eye health and digestion, along with small amounts of iron and protein. Ensure all kernels are popped to avoid choking hazards.
- Quinoa: This nutrient-dense grain is found in some high-quality dog foods and serves as a healthy alternative to common starches like corn, wheat, and soy.
- Wheat and Grains: Dogs do not necessarily need a grain-free diet. Grains such as wheat are good sources of protein, fiber, and essential fatty acids. However, if your dog has specific allergies, consult your veterinarian for personalized advice.
Proteins and Meats
- Eggs: Fully cooked eggs are a great source of protein and can help settle an upset stomach. Avoid feeding raw egg whites, as they can lead to biotin deficiency.
- Fish: Cooked fish, particularly salmon and sardines, offers beneficial fats and amino acids. Salmon is rich in vitamins and protein, while sardines provide digestible calcium from their bones. Always remove bones from other fish and ensure it is cooked thoroughly. Limit fish consumption to twice a week.
- Ham: While safe in small quantities, ham is high in sodium and fat and should not be a regular part of your dog’s diet.
- Pork: Pork is a highly digestible protein source rich in amino acids. It tends to be less allergenic for some pets compared to other meats and is a good alternative protein source.
- Shrimp: Fully cooked shrimp, with the shell removed, can be given as an occasional treat. They are packed with antioxidants, vitamin B-12, and phosphorus, while being low in fat and calories.
- Tuna: Small amounts of cooked, fresh tuna are beneficial due to omega-3 fatty acids. Canned tuna should be given sparingly due to its mercury and sodium content; choose tuna packed in water and without spices.
- Turkey: Plain turkey meat, with excess fat and skin removed, is safe. Always check for and remove bones, as they can splinter and cause internal injuries. Avoid any turkey prepared with salt, seasonings, onions, or garlic.
Dairy and Fats
- Cashews: Offer a few unsalted cashews at a time. They provide calcium, magnesium, and protein, but their fat content can lead to weight gain if given in excess.
- Cheese: Dogs can enjoy cheese in moderation if they are not lactose intolerant. Opt for lower-fat varieties like mozzarella or cottage cheese. Many dogs also enjoy specialized cheese-based dog chews.
- Coconut: Coconut, including its milk and oil, contains lauric acid, which can help fight bacteria and viruses. It may also improve skin conditions and reduce bad breath. Ensure the hard outer shell is kept away from your dog.
- Honey: Packed with nutrients and antioxidants, small amounts of honey can benefit dogs by helping to build immunity to local allergens. It can also be used topically for minor burns and cuts.
- Milk: While some dogs can tolerate milk, many are lactose intolerant. If you choose to offer milk, do so cautiously and be aware of potential digestive upset.
Fruits and Vegetables
- Peanuts: Unsalted peanuts are safe and provide good fats and proteins. Moderation is key to prevent excessive fat intake and potential pancreatic issues.
- Yogurt: Plain yogurt with active cultures can be a beneficial snack, offering probiotics that support digestive health. Avoid yogurts with added sugars or artificial sweeteners.
It’s important to introduce new foods gradually and monitor your dog for any signs of digestive upset. Always prioritize a balanced diet of high-quality dog food and consult your veterinarian if you have any concerns about your dog’s diet or specific health conditions. Remember, variety is good, but moderation and safety are paramount when sharing human foods with your canine companion.