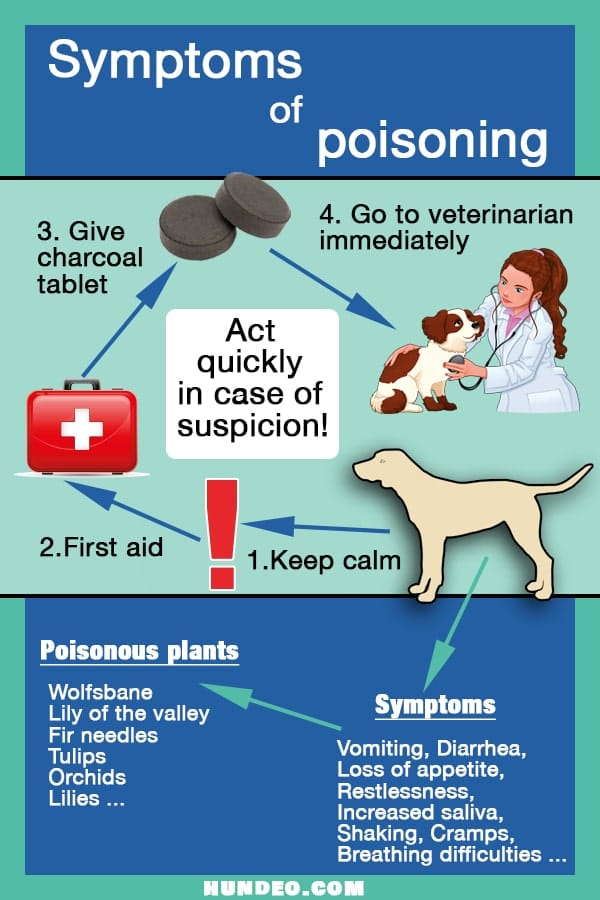
As devoted pet parents, we want to protect our canine companions from harm. Unfortunately, dogs’ natural curiosity can sometimes lead them into dangerous situations, especially concerning toxic substances. Poisoning can strike rapidly, turning a healthy dog into a critically ill patient within minutes. Being aware of the early warning signs of poisoning in dogs is crucial for timely intervention, potentially saving your beloved pet’s life. This guide will walk you through the key symptoms, what to do in an emergency, and how to prevent future poisoning incidents.
Understanding the Urgency: Immediate vs. Urgent Care
When your dog exhibits sudden, unusual symptoms, poisoning is a primary concern. Recognizing whether your dog needs immediate emergency care or urgent attention is the first step in getting them the help they need.
Signs Requiring Emergency Veterinary Care
Certain symptoms signal a critical emergency that demands immediate veterinary intervention. These include collapse, seizures, excessive drooling, significant breathing difficulties, severe vomiting, or bloody diarrhea. If your dog displays any of these alarming signs, contact a veterinary clinic without delay.
Symptoms Warranting Urgent Veterinary Attention
Beyond immediate emergencies, several other symptoms indicate your dog needs urgent care. These can include persistent vomiting, diarrhea, muscle tremors, marked behavioral changes, extreme lethargy, pale or bluish gums, rapid breathing, excessive thirst, or a loss of coordination. The combination and severity of these symptoms will help veterinarians determine the necessary speed of treatment.
Distinguishing Poisoning from Other Illnesses
It’s important to note that some symptoms of poisoning can mimic those of other health conditions, such as infections or kidney disease. However, if there’s any suspicion that your dog may have ingested or been exposed to a toxic substance, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and assume poisoning until a veterinarian confirms otherwise through diagnostic tests.
Common Causes of Poisoning in Dogs
Dogs are susceptible to poisoning from a wide array of everyday items. Their inquisitive nature, often leading them to explore with their mouths, puts them at constant risk. Common culprits include:
- Household items: Cleaning products, human medications (prescription and over-the-counter), and certain batteries.
- Foods: Chocolate, xylitol (an artificial sweetener found in gum, candy, and some peanut butters), grapes, raisins, onions, garlic, and avocado.
- Plants: Many common houseplants and garden plants are toxic to dogs, such as lilies, azaleas, sago palms, and oleander.
- Garden chemicals: Fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and rodenticides.
- Other: Antifreeze, certain types of mushrooms, and even insect bites or stings from venomous creatures.
Poisoning can occur through ingestion, skin contact with hazardous substances, or inhalation of toxic fumes.
Spotting the Subtle and the Severe
Poisoning symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening, depending on the toxin, the amount ingested, and the dog’s individual health.
Mild Signs of Poisoning
Early indicators of poisoning may not be dramatic. Look out for:
- Slightly increased drooling
- Mild, occasional vomiting or diarrhea
- A general decrease in energy or appetite
- Appearing slightly “off” or less enthusiastic than usual
Even these subtle changes should prompt a call to your veterinarian, as they can escalate quickly.
Recognizing Serious and Life-Threatening Cases
Severe poisoning presents with more alarming symptoms that require immediate attention:
- Continuous or violent vomiting and diarrhea (especially with blood)
- Difficulty breathing or labored breathing
- Seizures or convulsions
- Sudden collapse or extreme weakness
- Pale, white, blue, or bright red gums
- Muscle tremors or uncontrollable shaking
- Disorientation, confusion, or inability to stand
These severe signs indicate a critical situation where prompt veterinary care is essential.
What to Do If You Suspect Poisoning
Immediate action is critical when you suspect your dog has been poisoned. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Ensure Safety and Remove the Source
First, ensure your safety and your dog’s safety. Carefully move your dog away from the suspected toxic substance. Avoid direct contact with the substance using bare hands. If possible and safe to do so, identify what your dog may have ingested or been exposed to.
Step 2: Identify Key Warning Signs
Observe your dog closely and note any symptoms. This includes vomiting, drooling, trembling, changes in breathing, gum color, coordination, or behavior. Document when the symptoms began and how they are progressing.
Step 3: Contact a Veterinary Clinic Immediately
Call your veterinarian or an emergency animal hospital right away. Clearly describe the situation, including what you suspect your dog was exposed to and all observed symptoms. If you know the specific product or substance, provide that information. The veterinary team will advise you on the next steps, whether to bring your dog in immediately or if any home care is appropriate.
Step 4: Follow Professional Guidance Diligently
Adhere strictly to the veterinarian’s instructions. If you are told to bring your dog in, do so without delay. They may advise withholding food during acute vomiting episodes and only offering small sips of water if directed. Always follow their guidance on when to resume normal feeding and drinking habits.
Specific Dangers: Antifreeze, Rodenticides, Chocolate, and Caffeine
Some common household items pose particularly severe risks to dogs.
Antifreeze and Rodenticide Exposure
Antifreeze poisoning is particularly dangerous due to its sweet taste, which attracts dogs. Initial symptoms include staggering, excessive thirst, and vomiting. Without prompt treatment, it can lead to kidney failure and be fatal. Rodenticides (rat poisons) are designed to kill, and ingestion can cause severe internal bleeding. Signs include weakness, pale gums, and difficulty breathing. Both require immediate veterinary intervention. Signs of poisoning in dogs can manifest rapidly with these toxins.
Chocolate and Caffeine Ingestion
Chocolate and caffeine are stimulants that can cause significant harm to dogs. Symptoms include hyperactivity, rapid heart rate, tremors, and seizures. The darker the chocolate (baking chocolate, cocoa powder), the more concentrated the toxic compounds (theobromine and caffeine) are, making it more dangerous. The severity depends on the dog’s size and the amount consumed. Even small amounts can be life-threatening for smaller breeds. Understanding symptoms of a dog having a urinary tract infection is important, but recognizing these stimulant-related signs is critical for immediate action.
Supportive Care Before and After Veterinary Visits
While professional veterinary care is paramount, some supportive measures can be helpful, always under veterinary guidance.
Offering Water Cautiously
If your dog is experiencing vomiting, dehydration is a risk. If your veterinarian advises it, you can offer very small sips of water. Crucially, do not allow your dog to drink large amounts quickly, as this could trigger further vomiting. Always confirm with your vet before offering fluids.
Monitoring Neurological Changes
Pay close attention to your dog’s neurological status. Watch for any changes in coordination, alertness, pupil response, or muscle control. Signs like confusion, difficulty walking, head tilting, or twitching muscles can indicate that the poison is affecting the brain or nervous system, necessitating urgent veterinary care. Examining signs your dog has a bladder infection is different from recognizing these critical neurological signs.
Prevention: Safeguarding Your Home and Yard
The best approach to poisoning is prevention. By taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce the risk to your dog.
Securing Your Home Environment
- Medications and Chemicals: Store all human and pet medications, cleaning supplies, and household chemicals in secure cabinets or on high shelves that your dog cannot access.
- Toxic Foods: Keep all potentially toxic human foods completely out of reach. This includes chocolate, xylitol-containing products, grapes, raisins, onions, garlic, and alcohol.
- Trash Management: Use trash cans with secure, locking lids to prevent your dog from rummaging through garbage, which can contain harmful items.
Inspecting Your Yard and Garden
- Toxic Plants: Identify and remove any toxic plants from your yard and home that your dog might chew on. Familiarize yourself with common toxic plants in your region.
- Garden Products: Store fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and rodent baits in locked sheds or garages.
- Foraging Dangers: Regularly inspect your yard for wild mushrooms, which can be poisonous. Be especially vigilant after periods of rain. Securely store any gardening tools or equipment that may have residues of toxic substances. Paying attention to signs of bladder infection in male dogs is one aspect of health monitoring, but environmental safety is key to overall well-being.
When to Seek Help: Primary vs. Emergency Care
Understanding when to contact your regular veterinarian versus an emergency clinic is vital.
- Primary Veterinarian: For mild symptoms such as occasional vomiting, slight lethargy, or mild diarrhea, contact your primary veterinarian for advice. They can help assess the situation and determine if an in-clinic visit is necessary.
- Emergency Veterinary Clinic: For severe or rapidly worsening symptoms – including repeated vomiting, seizures, collapse, difficulty breathing, pale gums, or suspected ingestion of a highly toxic substance – call an emergency veterinary clinic immediately. Time is of the essence in these situations. Knowing the signs and symptoms of a UTI in dogs is helpful for general health, but severe symptoms always warrant immediate emergency care.
Our veterinary hospitals are fully equipped to handle poisoning emergencies, offering advanced diagnostic and treatment options. Specialty and emergency care centers provide the highest level of expertise for critical cases. When in doubt, always err on the side of caution and call us – we are here to help you through a stressful situation and provide guidance for your pet’s well-being.
Key Takeaways for Pet Owners
- Rapid Recognition is Key: Quickly identifying the signs of poisoning in dogs can be the difference between a successful recovery and a tragic outcome. Common indicators include vomiting, diarrhea, excessive drooling, tremors, and significant changes in behavior or energy levels.
- Secure Your Environment: Proactive prevention by securing all potential toxins—including medications, household chemicals, certain human foods, and toxic plants—away from your curious pet is paramount.
- Trust Your Instincts: As a pet parent, your intuition is valuable. If you observe anything that seems unusual or concerning about your dog’s health, seeking professional veterinary advice promptly is always the correct course of action.