Hookworms are a common and serious internal parasite affecting puppies and dogs, posing significant health risks if left untreated. While deworming medication is crucial for eliminating these parasites and restoring your pet’s health, it’s natural for pet parents to be concerned about potential adverse reactions. Understanding the Side Effects Of Hookworm Medicine For Dogs is essential for effective care, allowing you to recognize normal reactions from more serious issues and ensure your canine companion recovers smoothly.
The goal of hookworm treatment is to eradicate the parasites, preventing further blood loss, malnutrition, and environmental contamination. However, like all medications, dewormers can elicit a range of responses in dogs. Being informed about what to expect after administering the medication empowers you to provide the best possible post-treatment care and know when to seek veterinary assistance.
What Are Hookworms and Why Treatment is Crucial
Hookworms are tiny (about 1/8 inch long) intestinal parasites that get their name from their hook-like mouthparts. They attach to the lining of a dog’s small intestine and feed on blood, leading to blood loss and potentially severe anemia, especially in young puppies. These parasites are common throughout the United States, thriving in warm, moist environments.
Symptoms of hookworm infection can range from no visible signs to severe illness, including dark, tar-colored diarrhea, weight loss, pale gums, weakness, and anemia. In some cases, larvae migrating to the lungs can cause coughing, while skin penetration can lead to dermatitis between the toes. Prompt and accurate diagnosis by a veterinarian using a fresh stool sample is vital to confirm the presence of hookworms and rule out other intestinal parasites.
Treatment is critical not only for your dog’s health but also to prevent environmental contamination and potential transmission to other animals and even humans. Ignoring a hookworm infection can have dire consequences, making effective deworming an indispensable part of your dog’s healthcare.
Common Hookworm Medications and Their Mechanisms
Veterinarians typically prescribe anthelmintics (dewormers) to treat hookworm infections. These medications work by either paralyzing or killing the hookworms, allowing them to be passed out of the dog’s system, often in their stool. Common active ingredients found in hookworm medications include pyrantel pamoate, fenbendazole, milbemycin oxime, and moxidectin.
Many dewormers are available in various forms, such as oral tablets, chewables, or liquid suspensions. The choice of medication, dosage, and frequency of treatment depends on several factors, including the dog’s age, weight, overall health status, and the severity of the infection. Some preventative medications also offer comprehensive protection against multiple parasites, including hookworms, fleas, and ticks. For example, some products provide all in one worm and flea treatment for dogs, simplifying your pet’s parasite control regimen. Others might offer a more targeted 2 in 1 flea and worm treatment for dogs for specific needs.
Understanding the Side Effects: What to Expect
When administering hookworm medicine to your dog, it’s important to be aware of the potential side effects. These can range from mild and common reactions to less frequent but more serious concerns.
Mild and Common Side Effects
Most dogs tolerate deworming medication well, but some may experience mild, transient side effects as their body processes the medication and eliminates the parasites. These usually resolve within 24-48 hours.
- Gastrointestinal Upset: This is the most frequently observed side effect.
- Vomiting: Your dog might vomit shortly after taking the medication. This can be due to the taste of the medication, mild irritation of the stomach lining, or the body reacting to the dying parasites.
- Diarrhea: Loose stools or mild diarrhea are also common. As the dead or dying worms pass through the digestive tract, they can cause temporary digestive upset.
- Loss of Appetite: Some dogs may temporarily lose interest in food or show a decreased appetite after deworming.
- Lethargy: A slight decrease in energy or increased sleepiness is another common, mild reaction. This can be a general response to the body working to eliminate parasites or the medication itself.
These mild reactions are generally not cause for alarm unless they are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Less Common but More Serious Side Effects
While rare, some dogs may experience more significant adverse reactions to hookworm medication. These require immediate veterinary attention.
- Allergic Reactions: Like any medication, dewormers can cause allergic reactions. Signs may include:
- Facial swelling (especially around the eyes and muzzle)
- Hives or itchy skin
- Difficulty breathing (wheezing, labored breathing)
- Severe vomiting or diarrhea
- Collapse
- Neurological Issues: In very rare cases, certain deworming medications, particularly if overdosed or if the dog has a specific genetic sensitivity (e.g., MDR1 gene mutation in some herding breeds), can cause neurological symptoms. These might include:
- Ataxia (wobbly gait or loss of coordination)
- Tremors
- Seizures
- Disorientation
- Severe Gastrointestinal Distress: While mild vomiting and diarrhea are common, severe or bloody vomiting/diarrhea, especially if prolonged, is a sign that something more serious may be occurring and warrants immediate veterinary consultation.
- Worsening of Underlying Conditions: For dogs with pre-existing health issues, deworming medication could potentially exacerbate those conditions. It is crucial to inform your veterinarian of your dog’s complete medical history.
It’s important to differentiate these serious reactions from the more typical mild side effects of hookworm medicine for dogs. If you observe any of these severe signs, contact your veterinarian immediately.
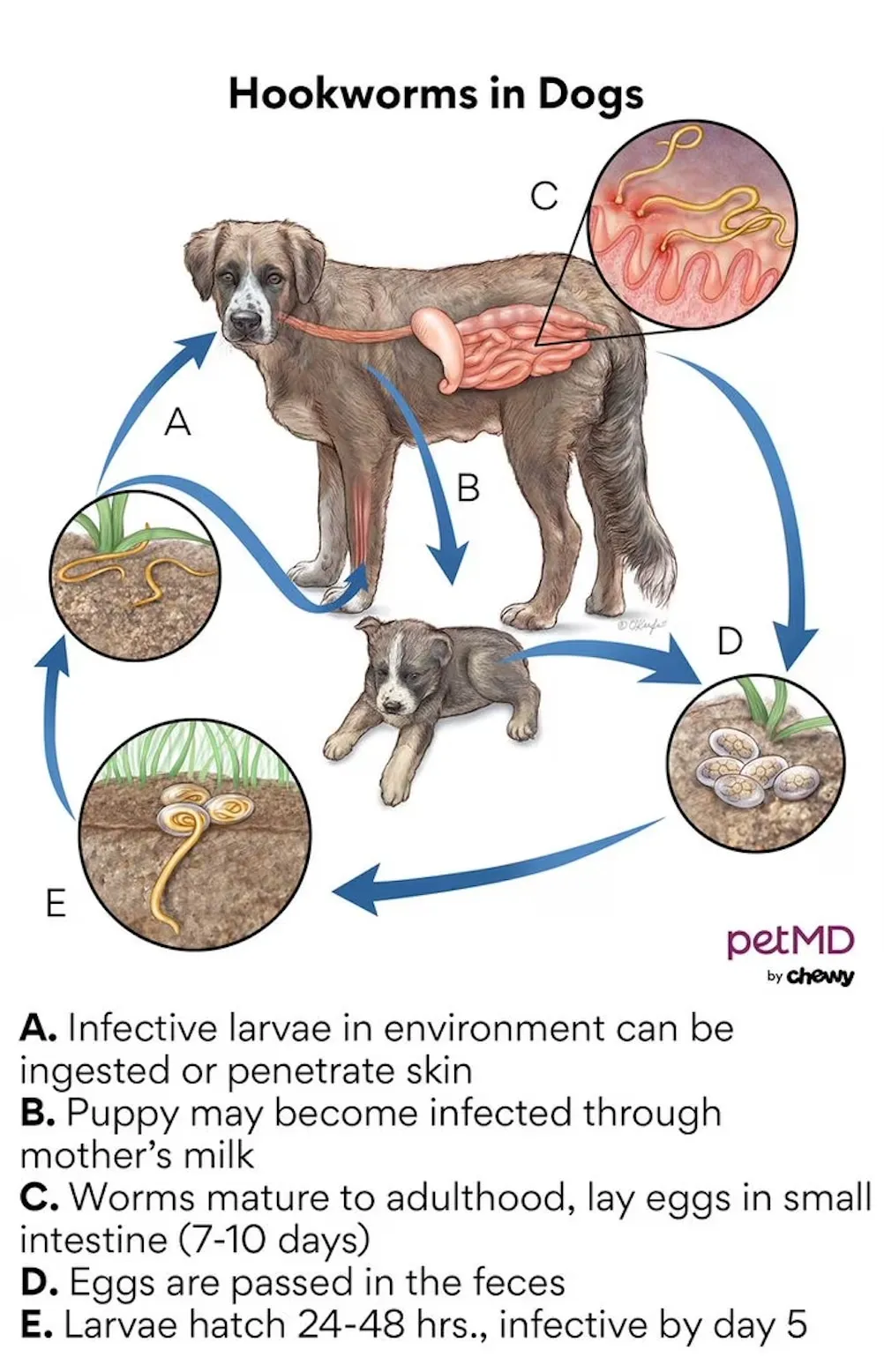 Diagram showing hookworm infection in canine digestive system
Diagram showing hookworm infection in canine digestive system
When to Contact Your Veterinarian
Knowing when to call your vet is key to managing the side effects of hookworm medication.
Contact your vet immediately if you observe any of the following:
- Severe or persistent vomiting or diarrhea: Especially if it’s bloody, lasts for more than 24-48 hours, or is accompanied by other severe symptoms.
- Signs of an allergic reaction: Facial swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, or collapse.
- Neurological symptoms: Tremors, seizures, disorientation, or severe incoordination.
- Extreme lethargy or weakness: Your dog is unable to stand, unresponsive, or appears significantly sicker than expected.
- Any unusual or concerning behavior: If your dog seems in severe pain, is unusually agitated, or displays symptoms you haven’t seen before.
For mild, transient side effects like slight lethargy or a single episode of vomiting, you might monitor your dog closely. However, if you are ever in doubt, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and contact your veterinary clinic for advice. This is especially true if you are also managing other parasite issues, as combined treatments like a flea tick and intestinal worm treatment for dogs can sometimes have varied reactions.
Minimizing Side Effects and Ensuring Safe Treatment
While some side effects are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to help minimize their impact and ensure the safest possible treatment for your dog.
- Follow Dosage Instructions Precisely: Always administer the medication exactly as prescribed by your veterinarian. Never guess the dosage or give more than recommended, as overdosing significantly increases the risk of severe side effects.
- Administer with Food (Unless Directed Otherwise): Many dewormers can be given with a meal to help reduce stomach upset. Always check the medication instructions or ask your vet if the dewormer should be given with or without food.
- Monitor Your Dog Closely: For the first 24-48 hours after treatment, keep a close eye on your dog. Note any changes in behavior, appetite, or gastrointestinal function. This vigilance allows you to catch any severe reactions early.
- Ensure Hydration: If your dog experiences vomiting or diarrhea, ensure they have access to fresh water to prevent dehydration. Small, frequent amounts of water can be better tolerated than large quantities at once.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Hookworm eggs are shed in feces. Promptly remove and dispose of all stool from your home and yard to prevent re-infection and contamination. Cleaning bedding and toys can also reduce the environmental parasite load. Regular cleaning is critical, especially if you’re also dealing with treatments like a flea worm and mite treatment for dogs, which emphasizes overall parasite control.
Importance of Veterinary Guidance and Follow-up
The most critical aspect of managing hookworm infection and its treatment side effects is ongoing collaboration with your veterinarian. They can:
- Provide an accurate diagnosis: Ensuring your dog is treated for the correct parasite.
- Prescribe the appropriate medication and dosage: Tailored to your dog’s specific needs and health status.
- Offer guidance on administration: Explaining how and when to give the medication.
- Advise on what to expect: Informing you about common and rare side effects.
- Conduct follow-up tests: Fecal re-examinations are often necessary to confirm the treatment’s effectiveness and ensure all parasites have been eliminated. This is particularly important because hookworms can develop resistance to dewormers over time.
Never hesitate to reach out to your vet with questions or concerns about the side effects of hookworm medicine for dogs. Their expertise is invaluable in safeguarding your pet’s health.
Prevention: A Proactive Approach to Hookworm Management
The best way to avoid the stress of treating hookworms and managing potential side effects is through proactive prevention.
- Monthly Parasite Preventatives: Many broad-spectrum monthly preventatives protect against hookworms, heartworms, and other intestinal parasites. Discuss with your veterinarian which product is best suited for your dog’s lifestyle and risk factors.
- Regular Fecal Exams: Even with preventatives, annual or biannual fecal examinations are recommended to monitor for parasites. Puppies and newly adopted dogs may require more frequent testing.
- Good Hygiene: Promptly removing dog feces from your yard and public spaces prevents the spread of hookworm eggs. Avoid walking your dog in areas known to be heavily contaminated.
- Deworming Pregnant and Nursing Dogs: Your vet may recommend deworming pregnant or nursing dogs to minimize the risk of transmission to puppies.
By adhering to these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your dog’s risk of hookworm infection and the subsequent need for treatment.
Conclusion
Hookworm medication is a vital tool for protecting your dog from the dangers of parasitic infection. While understanding the potential side effects of hookworm medicine for dogs is crucial for responsible pet ownership, most reactions are mild and temporary. Being prepared for common symptoms like mild vomiting or lethargy, and knowing when to seek immediate veterinary help for more serious signs, ensures your dog receives optimal care. Always work closely with your veterinarian to ensure accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and ongoing prevention strategies to keep your canine companion healthy and parasite-free.
References
- Companion Animal Parasite Council (CAPC). (Updated March 29, 2023). Hookworms.
- PetMD. (Accessed various pages for context). Hookworms in Dogs: Symptoms, Treatment, and How to Prevent Them.
- Merck Manual. (Revised October 2023). Cutaneous Larva Migrans.
- Veterinary Practice News. (Published December 22, 2022). Hookworms are becoming resistant to treatment – what now?
