The male reproductive system in dogs is a complex and fascinating subject. Understanding its components and how they function is crucial for responsible dog ownership, especially for breeders or those interested in canine health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the male dog’s reproductive anatomy and physiology, providing valuable insights for dog owners.
Similar to the dog reproductive anatomy female, the male reproductive system plays a vital role in the continuation of the canine species. From the testicles where sperm is produced to the penis which facilitates mating, each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall reproductive process. We’ll explore these components in detail, covering their structure, function, and common health issues. This understanding will not only benefit breeders but also help pet owners make informed decisions about their dog’s health and well-being.
Key Components of the Male Dog Reproductive System
The male dog’s reproductive system comprises several key components, each playing a crucial role in the production, maturation, and delivery of sperm. Let’s break down these components and their functions.
The Testicles: Sperm Production Hub
The testicles, also known as testes, are the primary reproductive organs in male dogs. They are responsible for producing sperm and the male sex hormone, testosterone. Located within the scrotum, a sac of skin that hangs outside the body, the testicles are kept at a slightly lower temperature than the body’s core temperature, which is essential for optimal sperm production.
The Epididymis: Sperm Maturation Site
After being produced in the testicles, sperm travels to the epididymis, a coiled tube located adjacent to each testicle. Within the epididymis, sperm matures and gains the ability to swim, preparing them for their journey to fertilize an egg.
The Vas Deferens: Sperm Transport Channel
The vas deferens, also known as the ductus deferens, is a muscular tube that connects the epididymis to the urethra. Its primary function is to transport mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
The Prostate Gland: Seminal Fluid Contributor
The prostate gland, located near the bladder, is responsible for producing a significant portion of the seminal fluid. This fluid nourishes and protects the sperm, aiding in their survival and motility.
The Penis: The Organ of Copulation
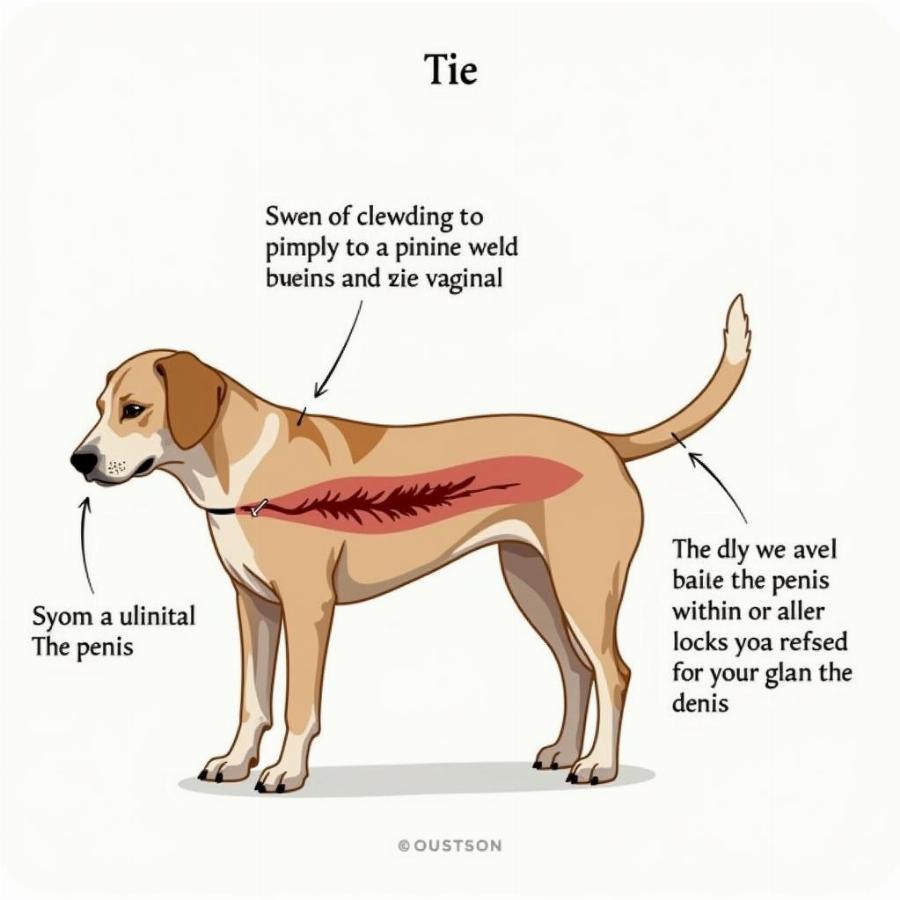
The penis is the male organ of copulation, responsible for delivering sperm into the female reproductive tract during mating. The canine penis has a unique structure, featuring a bone called the os penis, which provides rigidity during mating. The bulbus glandis, located at the base of the penis, swells during mating, creating the “tie” that is characteristic of canine copulation.
Common Health Concerns in the Male Dog Reproductive System
Just like any other body system, the male reproductive system in dogs is susceptible to various health issues. Understanding these potential problems can help dog owners seek timely veterinary care and ensure their dog’s reproductive health.
Cryptorchidism: Undescended Testicles
Cryptorchidism is a condition where one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum. This can lead to infertility and an increased risk of testicular cancer.
Testicular Cancer: Malignant Growth in the Testicles
Testicular cancer is a relatively common malignancy in male dogs. Regular palpation of the testicles can help detect any abnormalities early on.
Prostatitis: Inflammation of the Prostate Gland
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by bacterial infections. Symptoms can include difficulty urinating, pain, and fever.
How Does the Male Dog Reproductive System Compare to the Female’s?
While both systems contribute to reproduction, they have distinct roles and structures. The male system focuses on sperm production and delivery, while the female system is responsible for egg production, fertilization, and gestation. Understanding these differences is crucial for responsible breeding practices. Learn more about the dog female reproductive system to gain a comprehensive understanding of both sides of canine reproduction.
What is the role of testosterone in the male dog?
Testosterone, produced by the testicles, plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of male characteristics, such as muscle mass, bone density, and libido. It also plays a vital role in sperm production.
How does the “tie” occur during mating?
The “tie” during mating is caused by the swelling of the bulbus glandis, a structure at the base of the penis. This swelling locks the penis within the female’s vagina, ensuring efficient sperm transfer.
 Dog Mating Tie Illustration
Dog Mating Tie Illustration
Caring for Your Male Dog’s Reproductive Health
Maintaining your male dog’s reproductive health is essential for his overall well-being. Regular veterinary checkups, including testicular examinations, can help detect potential problems early on. Neutering, while a personal choice, can significantly reduce the risk of certain reproductive health issues, such as testicular cancer and prostate problems. For a deeper understanding of the female counterpart, you can refer to the article on canine female reproductive anatomy.
What are the benefits of neutering a male dog?
Neutering can reduce the risk of testicular cancer, prostate problems, and certain behavioral issues, such as roaming and aggression. It also helps control the dog population.
How often should I have my male dog’s reproductive system checked?
Annual veterinary checkups, including testicular examinations, are recommended for all male dogs.
Conclusion
Understanding the male reproductive system of the dog is crucial for responsible dog ownership. This knowledge empowers owners to make informed decisions about their dog’s health, breeding practices, and overall well-being. By learning about the intricate workings of this system, we can better care for our canine companions and ensure their continued health and happiness. For those interested in a comparative perspective, the information on female dog reproductive parts may be helpful.
FAQs
- What is the main function of the male reproductive system of a dog? The primary function is to produce and deliver sperm for reproduction.
- What are the two main functions of the testicles? The testicles produce sperm and the hormone testosterone.
- Where does sperm mature? Sperm matures in the epididymis.
- What is the role of the prostate gland? The prostate gland contributes to the production of seminal fluid.
- What causes the “tie” during mating? The swelling of the bulbus glandis at the base of the penis causes the “tie”.
- What is cryptorchidism? Cryptorchidism is a condition where one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum.
- What are the benefits of neutering? Neutering can reduce the risk of testicular cancer, prostate problems, and certain behavioral issues. For further understanding of the female system, refer to this resource on the reproductive system female dog.
