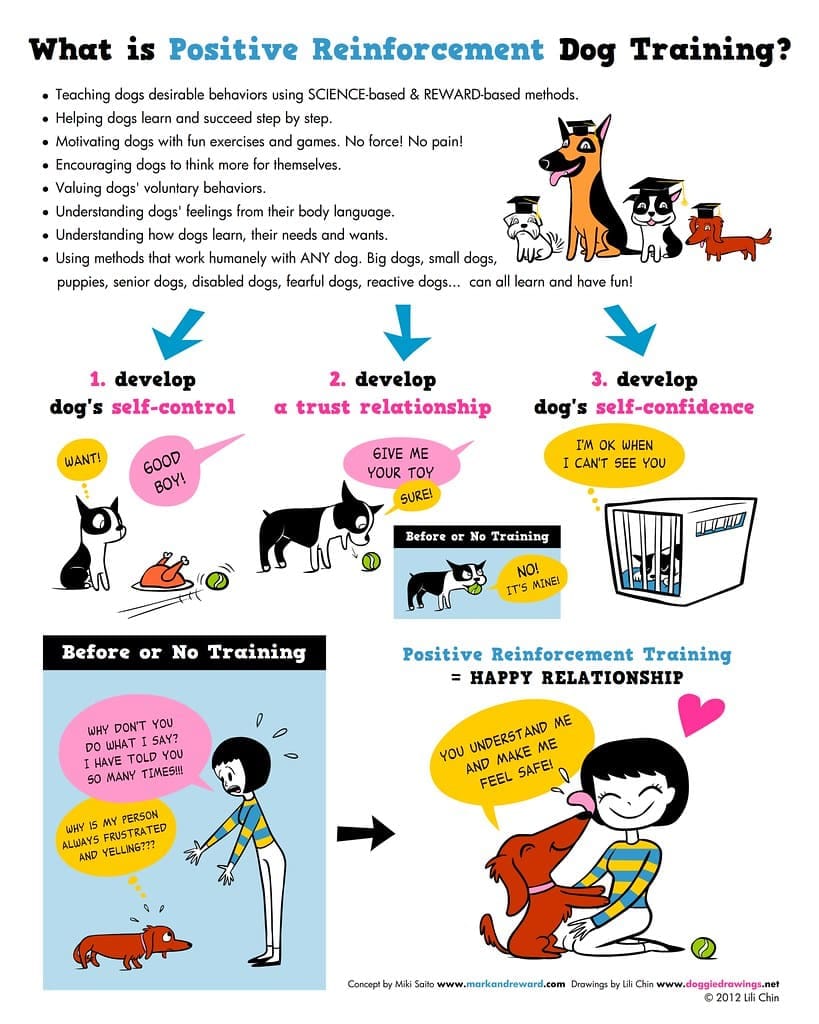
Are you looking for the best ways to train your canine companion? Understanding the fundamentals of dog training is crucial for a harmonious life with your pet. This guide delves into the essential aspects of dog training, drawing insights that can be applied universally, whether you’re considering programs at the Licking County Humane Society or implementing positive reinforcement at home. Effective training builds a stronger bond between you and your dog, fostering good behavior and preventing common issues.
Understanding Dog Behavior and Communication
Before diving into specific training techniques, it’s vital to understand how dogs communicate and what drives their behavior. Dogs often use a combination of body language, vocalizations, and scent to express themselves. Recognizing signs of stress, happiness, fear, or aggression is the first step in addressing training challenges effectively.
- Body Language: A wagging tail doesn’t always mean happiness; context is key. A stiff body, raised hackles, or a direct stare can indicate arousal or potential aggression.
- Vocalizations: Barks, growls, and whimpers all convey different messages. Learning to differentiate these sounds can help you respond appropriately to your dog’s needs.
- Basic Needs: Ensure your dog’s fundamental needs for food, water, shelter, exercise, and mental stimulation are met. Unmet needs can often manifest as behavioral problems.
Essential Dog Training Principles
Positive reinforcement is widely recognized as the most effective and humane approach to dog training. This method focuses on rewarding desired behaviors, making them more likely to occur in the future.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
- Reward-Based Training: When your dog performs a desired action (like sitting when asked), immediately reward them with a high-value treat, praise, or a favorite toy. This creates a positive association with the command.
- Timing is Crucial: Rewards should be delivered within seconds of the desired behavior so your dog clearly understands what they are being rewarded for.
- Consistency: Everyone in the household should use the same commands and reward system to avoid confusing the dog.
- Patience: Every dog learns at a different pace. Be patient and celebrate small successes.
Introducing Basic Commands
Starting with fundamental commands provides a solid foundation for more advanced training.
- “Sit”: Hold a treat near your dog’s nose and move it upwards and slightly back over their head. As their head follows the treat, their rear end should naturally lower into a sit.
- “Stay”: Once your dog masters “sit,” ask them to stay, hold up your hand in a “stop” signal, and take a step back. Gradually increase the distance and duration before rewarding.
- “Come”: Use a cheerful tone and an open stance to call your dog. Reward them enthusiastically when they reach you. Never punish your dog if they eventually come, as this will discourage them from responding in the future.
- “Down”: From a sit position, lure your dog down by moving a treat from their nose towards the floor and slightly away from them.
Addressing Common Behavioral Issues
Even with consistent training, some dogs may exhibit challenging behaviors. Professional guidance can be invaluable in these situations.
Leash Reactivity and Pulling
Many dogs pull on the leash, making walks unpleasant. This often stems from excitement or a lack of training.
- Technique: When your dog pulls, stop walking. Only resume when the leash slackens. Alternatively, change direction whenever the leash becomes taut.
- Equipment: Consider using a front-clip harness or a head halter for better control, but these should be introduced gradually and positively.
Barking
Excessive barking can be a nuisance and may indicate underlying issues like boredom, anxiety, or a territorial response.
- Management: Identify the trigger for the barking. If it’s excitement, manage their environment to reduce stimuli. If it’s anxiety, focus on building their confidence and security.
- Training: Teach a “quiet” command by rewarding moments of silence after barking.
Separation Anxiety
This is a more serious behavioral issue where dogs become distressed when left alone. Symptoms include destructive behavior, excessive barking, and house soiling.
- Professional Help: Separation anxiety often requires professional intervention. Consult with a veterinarian or a certified professional dog trainer specializing in behavior modification.
- Desensitization: Gradually acclimate your dog to your departures by starting with very short absences and increasing the duration slowly.
The Role of Local Resources like Licking County Humane Society
Organizations like the Licking County Humane Society often provide valuable resources for dog owners. They may offer:
- Training Classes: Group classes can be cost-effective and provide socialization opportunities for your dog. They cover basic obedience and can address common behavioral problems.
- Behavioral Consultations: Some shelters offer one-on-one consultations with experienced trainers or behaviorists to tackle specific issues.
- Adoption Support: If you’re considering adopting a dog, these organizations can provide guidance on choosing the right pet and offer post-adoption support.
Advanced Training and Dog Sports
Once your dog has mastered basic obedience, you might consider more advanced training or dog sports. These activities offer excellent mental and physical stimulation and further strengthen your bond.
- Agility: Navigating obstacle courses designed for dogs.
- Nose Work: Utilizing a dog’s natural scenting abilities to find hidden “targets.”
- Canine Good Citizen (CGC): A certification program that tests a dog’s manners and obedience in real-world settings.
Creating a Supportive Training Environment
A successful training journey requires more than just commands and rewards. It involves building trust, understanding, and a positive relationship with your dog.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: A tired dog is often a well-behaved dog. Ensure your dog gets adequate physical exercise and engaging mental activities, such as puzzle toys or scent games.
- Socialization: Exposing your puppy or dog to various people, environments, and other well-behaved dogs during their critical developmental periods is crucial for building confidence and preventing fear-based behaviors. This is a key area where programs at places like Licking County Humane Society can be instrumental.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet plays a significant role in a dog’s overall health and behavior. Consult your veterinarian about the best food options for your dog’s age, breed, and activity level.
Conclusion: The Lifelong Journey of Dog Training
Dog training is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that evolves with your dog throughout their life. By applying positive reinforcement techniques, understanding your dog’s communication, and seeking resources like those offered by the Licking County Humane Society, you can build a fulfilling and joyful relationship with your canine companion. Remember that consistency, patience, and a deep understanding of your dog’s needs are the cornerstones of successful and compassionate dog training.