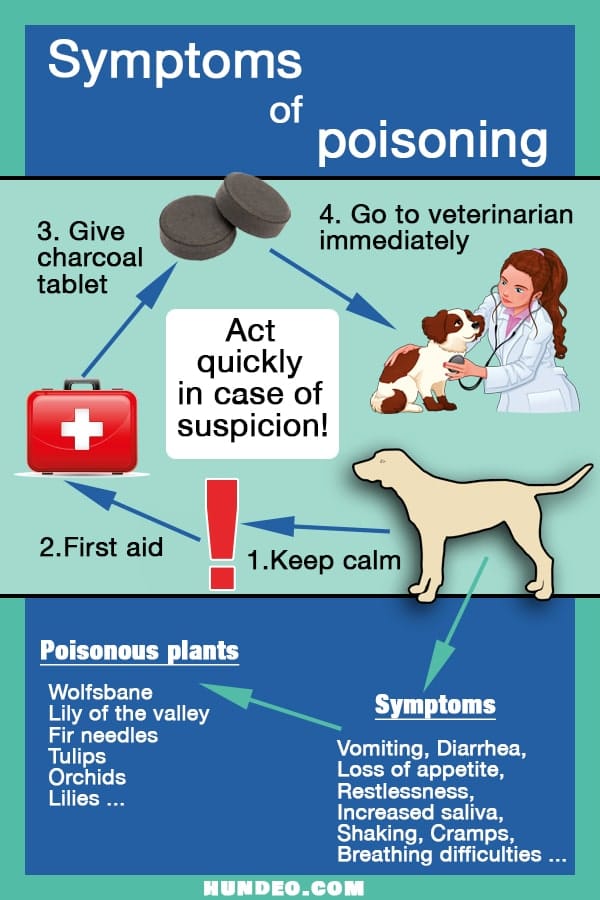
When your beloved canine companion suddenly exhibits unusual symptoms, it’s natural to feel a surge of worry. Dogs can deteriorate rapidly after ingesting a toxic substance, making swift recognition of poisoning signs critical. This guide will help you identify early indicators and know the crucial steps to take, potentially turning a critical emergency into a treatable situation.
Understanding the Urgency: Key Questions Answered
Is My Dog in Immediate Danger?
Several symptoms signal an immediate threat to your dog’s life, demanding emergency veterinary intervention. These include collapse, seizures, excessive drooling, difficulty breathing, and severe, persistent vomiting or diarrhea. If you observe any of these alarming signs, contact a veterinary clinic without delay.
Which Symptoms Require Urgent Care?
Beyond the most critical indicators, other symptoms also warrant immediate veterinary attention. These include recurring vomiting, bloody diarrhea, muscle tremors, significant behavioral changes, extreme lethargy, and pale or bluish gums. Rapid respiration, excessive thirst, or a loss of coordination can also point to poisoning. The combination and intensity of these signs help determine the urgency of the situation.
Could These Symptoms Be Something Else?
It’s true that certain illnesses, such as infections or kidney disease, can mimic the symptoms of poisoning. However, if there’s any possibility your dog has come into contact with a harmful substance, it is always safest to assume poisoning and seek veterinary advice. A veterinarian can conduct diagnostic tests to pinpoint the exact cause of your dog’s condition.
Common Causes of Dog Poisoning
Dogs are naturally curious and often explore their environment with their mouths, putting them at risk of ingesting various household toxins. These can include common cleaning products, human medications, certain human foods (like chocolate, grapes, or xylitol), houseplants, and garden chemicals. Poisoning can also occur through skin absorption of toxic substances or inhalation of toxic fumes.
Spotting Mild Warning Signs
Early indications of poisoning in dogs might be subtle. You may notice mild vomiting, slightly increased drooling, or a general decrease in energy. Your dog might also show less interest in food, experience mild diarrhea, or simply seem “off” or unwell. Even these minor changes should prompt a call to your veterinarian, as what appears mild can quickly escalate.
Recognizing Severe Poisoning Indicators
More serious poisoning signs include intense, unrelenting vomiting or diarrhea, significant breathing difficulties, seizures, or complete collapse. A change in gum color to very pale, blue, or an unusually bright red, excessive salivation, or drastic behavioral shifts are also critical concerns. Tremors, profound weakness, disorientation, or an inability to stand are clear indicators that immediate veterinary care is essential.
Immediate Steps to Take
Step 1: Remove Your Dog from the Source
As soon as you suspect your dog has encountered a toxic substance, carefully move them away from the area. It’s advisable to avoid direct contact with any suspicious materials using your bare hands. If you can safely identify what your dog may have ingested, note it down, but do not put yourself at risk to do so.
Step 2: Assess for Key Warning Signs
Closely observe your dog for symptoms such as vomiting, excessive drooling, trembling, or unusual breathing patterns. Note any changes in gum color, coordination issues, or peculiar behaviors. It is also important to keep track of when the symptoms began and how they are progressing.
Step 3: Contact a Veterinary Clinic
Contact a veterinary clinic immediately, regardless of whether the symptoms appear mild or severe. Clearly describe the circumstances and any symptoms you have observed. If you know what your dog ingested, provide that information. Inquire whether you should bring your dog in for immediate examination or if there are any first-aid steps you can take at home.
Step 4: Follow Professional Guidance
Adhere strictly to the instructions provided by the veterinarian. If they advise bringing your dog in, do so without delay. In cases of acute vomiting, withhold food and offer only small sips of water if specifically recommended. For guidance on when to resume normal feeding and drinking, consult your veterinary clinic first.
Potential Life-Threatening Conditions
Antifreeze or Rodenticide Exposure
Ingestion of antifreeze can initially lead to staggering, excessive thirst, and vomiting. Rodenticides, or rat poison, can cause severe internal bleeding, manifesting as weakness, pale gums, and difficulty breathing. Both of these toxins are extremely dangerous and require rapid veterinary treatment. If you suspect your dog has ingested either substance, contact a veterinary clinic immediately.
Chocolate or Caffeine Ingestion
Consuming chocolate or caffeine can induce hyperactivity, an elevated heart rate, tremors, and even seizures in dogs. The darker the chocolate, the higher the concentration of toxic compounds. The severity of the reaction depends on your dog’s size and the amount ingested. Even small quantities of baking chocolate or cocoa powder can be hazardous for smaller breeds.
Supporting Your Pet Before Veterinary Arrival
Offering Small Amounts of Water
If your dog is experiencing vomiting, they are at risk of dehydration. Offering small sips of water may be appropriate if advised by your veterinarian. Crucially, do not let your dog drink large volumes at once, as this could trigger further vomiting. Always seek veterinary guidance before offering water.
Monitoring for Neurological Changes
Pay close attention to any changes in your dog’s coordination, alertness, or muscle control. Note if your dog appears disoriented, has trouble walking, or exhibits muscle tremors. These neurological signs can indicate that the ingested poison is affecting the brain or nervous system, necessitating prompt veterinary care.
Preventing Future Poisoning Incidents
Securing Your Home Environment
Ensure all medications, cleaning supplies, and household chemicals are stored in secure cabinets inaccessible to your dog. Keep toxic human foods such as chocolate, grapes, raisins, xylitol, and onions well out of reach. Use trash cans with locking lids to prevent your dog from rummaging through garbage.
Inspecting Your Yard and Garden
Remove any toxic plants, such as lilies, azaleas, and sago palms, from areas where your dog has access. Store fertilizers, insecticides, and rodent baits in a safe, locked location. Regularly inspect your yard for wild mushrooms, which can be particularly toxic to dogs, especially after periods of rain.
Expert Assistance is Available
If your dog displays minor symptoms like occasional vomiting or slight lethargy, contact your regular veterinarian for advice. For severe or rapidly worsening symptoms—including persistent vomiting, seizures, collapse, or breathing difficulties—seek immediate attention at an emergency veterinary clinic. Our hospitals are equipped with advanced facilities to manage poisoning cases effectively. The benefit of accessing specialty and emergency care ensures your dog receives the most advanced treatment available when critical. When in doubt, always call us; we can guide you through the situation.
Key Takeaways
- Swift Recognition is Vital: Quickly identifying the signs of poisoning in dogs can be life-saving. Common symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, drooling, tremors, and changes in behavior or energy levels.
- Secure Potential Toxins: Always keep medications, chemicals, certain foods, and toxic plants out of your dog’s reach.
- Trust Your Instincts: As a devoted pet parent, if you sense something is amiss with your dog’s health, seeking professional veterinary advice is always the most responsible course of action.