Hypothyroidism is a prevalent endocrine condition affecting dogs, characterized by the decreased production of thyroid hormones essential for regulating metabolism. These hormones, produced by the thyroid glands located in the neck, play a crucial role in various bodily functions. When thyroid hormone levels are insufficient, a dog’s overall body functions begin to slow down.
The most common underlying causes of hypothyroidism in dogs are inflammation of the thyroid glands, known as lymphocytic thyroiditis, or degeneration of the thyroid gland, referred to as idiopathic thyroid gland atrophy. Fortunately, thyroid tumors are relatively rare in canine patients. This condition typically affects middle-aged dogs, with medium to large breeds being more susceptible. Certain breeds, including Golden Retrievers, Dobermans, Dachshunds, Miniature Schnauzers, Cocker Spaniels, and Irish Setters, show a higher predisposition to developing hypothyroidism.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Dogs suffering from hypothyroidism often exhibit a range of clinical signs. One of the most noticeable is weight gain, frequently occurring without any increase in appetite. Pet parents often observe their dog gaining considerable weight despite a seemingly normal food intake.
Another common symptom is lethargy and laziness. Affected dogs may prefer to rest and sleep throughout the day, showing a diminished interest in playing or exercising. Due to their slowed metabolism, dogs with hypothyroidism often feel colder than usual, leading to heat-seeking behavior. They might gravitate towards fireplaces or heating vents to maintain their body temperature.
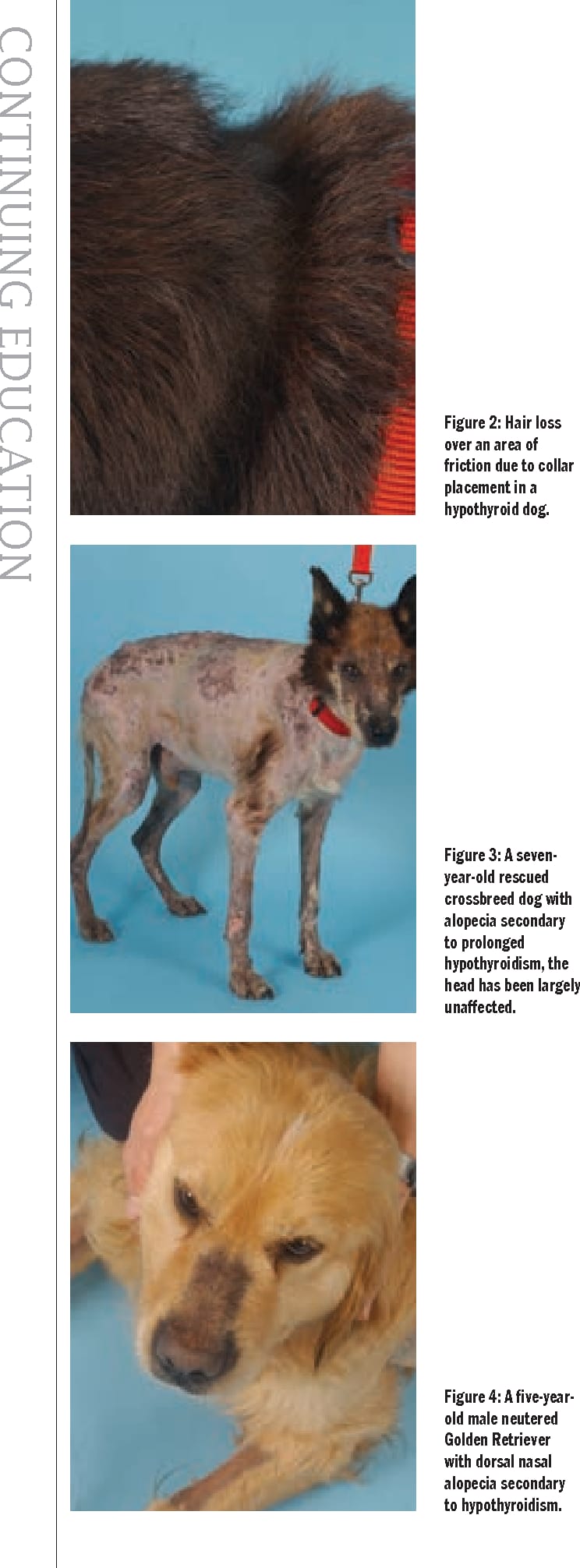
Chronic skin and ear infections can also be indicative of an underlying issue like hypothyroidism, although allergies are also a common cause. The dog’s coat may become dry and brittle, with noticeable thinning of the hair, particularly on the back and tail, sometimes giving the tail a “rat tail” appearance. Changes in skin pigmentation and an inability to regrow hair after shaving are also observed in some cases.
Less common symptoms can include reproductive problems or neurological issues, such as nerve pain or hind leg weakness. Some dogs may develop small, white fatty deposits on their eyes or suffer from dry eye, a condition where tear production is insufficient. In severe cases, the facial skin may thicken, causing a drooping appearance to the facial muscles.
The Causes Behind Canine Hypothyroidism
As mentioned, the primary culprits behind hypothyroidism are lymphocytic thyroiditis and idiopathic thyroid gland atrophy. While the exact reasons these conditions arise spontaneously remain unclear, a genetic predisposition is known to exist. Cancer is a rare cause of hypothyroidism, accounting for a small fraction of cases. In the majority of instances, management with medication is effective for both inflammation and degeneration of the thyroid gland.
Veterinary Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
A veterinarian’s diagnostic process begins with a thorough physical examination and a detailed review of the dog’s medical history. Providing information about any unusual behaviors or physical changes, along with their onset, is crucial. Basic blood work and urinalysis may be performed to assess the dog’s overall health. If skin issues are present, skin scrapings or smears might be conducted to rule out secondary infections.
The definitive diagnosis of hypothyroidism is made through blood tests. Veterinarians commonly use a screening test called a total thyroxine level (Total T4, or TT4) to measure the primary thyroid hormone. A low TT4 level, combined with clinical signs, strongly suggests hypothyroidism. To confirm the diagnosis, particularly in cases with borderline TT4 levels, veterinarians may order additional tests such as a free T4 level or a full thyroid panel.
Treatment and Management of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is effectively managed with an oral medication called levothyroxine, a synthetic replacement for the missing thyroid hormone. It is crucial to understand that hypothyroidism is treatable, not curable, and requires lifelong medication.
Your veterinarian will prescribe the appropriate dosage of levothyroxine based on your dog’s weight, and a follow-up blood test in about a month is usually recommended to ensure the dosage is correct. Untreated hypothyroidism can significantly impact a dog’s lifespan, as thyroid hormones affect nearly every organ system. Such dogs may develop high cholesterol, weakened immune function, a slowed heart rate, and neuromuscular problems, including unsteadiness, head tilts, and even seizures. Prompt and proper treatment, however, leads to a significant improvement in a dog’s quality of life.
Ongoing Care and Prognosis
Lifelong oral thyroid hormone replacement therapy is essential for managing hypothyroidism in dogs. Regular monitoring of blood thyroid levels, typically every 6 to 12 months, is recommended to ensure the dog remains on the correct medication dosage, as metabolism and tolerance can change over time.
Once thyroid levels normalize, dogs often experience weight loss as their body condition improves and a noticeable increase in energy. While it may take several months for hair to regrow fully, improvements in skin and coat quality are expected. Owners should also monitor their dog’s eyes for any signs of decreased tear production, such as green-yellow discharge, and consult their veterinarian if any changes are observed.
Frequently Asked Questions About Canine Hypothyroidism
Is hypothyroidism curable?
No, hypothyroidism is a manageable condition, not a curable one. Treatment involves lifelong oral synthetic thyroid hormone replacement.
Can thyroid medication be overdosed?
Yes, thyroid medication can be overdosed. It is critical that your dog receives the correct dosage. Your veterinarian will carefully adjust the dose, potentially requiring multiple re-check appointments. Signs of an overdose include excessive weight loss, irritability, increased thirst and panting, and sleeplessness.
What is the life expectancy of a dog with hypothyroidism?
Dogs with well-managed hypothyroidism can lead normal, healthy lives with an excellent prognosis and a normal life expectancy.