Hot spots, medically known as acute moist dermatitis, are a common and distressing skin condition for dogs, often appearing in areas prone to irritation, such as the tail. These painful, red, and inflamed lesions can develop rapidly, causing discomfort and potentially leading to more severe issues if not addressed promptly. Understanding how to identify, treat, and prevent hot spots on your dog’s tail is crucial for their well-being. This guide will provide you with the essential knowledge to manage and heal these vexing skin irritations, ensuring your canine companion remains happy and healthy.
What Are Hot Spots and Why Do They Appear on a Dog’s Tail?
Hot spots are localized areas of skin inflammation and infection that appear as moist, red, and often painful lesions. While they can occur anywhere on a dog’s body, the tail is a particularly susceptible area due to several factors. The tail’s constant movement, its proximity to the anal glands (which can become irritated), and the potential for it to be wet for extended periods (especially in swimming dogs) create an environment ripe for hot spot development.
Dogs will typically chew, lick, or scratch intensely at the affected area, exacerbating the irritation and rapidly enlarging the lesion. This self-trauma prevents the skin from healing and introduces bacteria, leading to a secondary infection. The fur around the hot spot becomes matted with exudate, trapping moisture and further hindering recovery. For more general information on how to heal a hot spot on a dog, understanding these basic principles is key.
Identifying a Hot Spot on Your Dog’s Tail
Recognizing a hot spot on your dog’s tail early is vital for effective treatment. Look for the following signs:
- Redness and inflammation: The skin will appear bright red and swollen.
- Moisture or oozing: The area will often be wet, and there might be a discharge.
- Hair loss: Fur around the lesion will be matted or completely absent.
- Pain: Your dog may react negatively when you touch the area.
- Intense itching: Excessive licking, chewing, or scratching at the tail.
- Odor: A foul smell can indicate a bacterial infection.
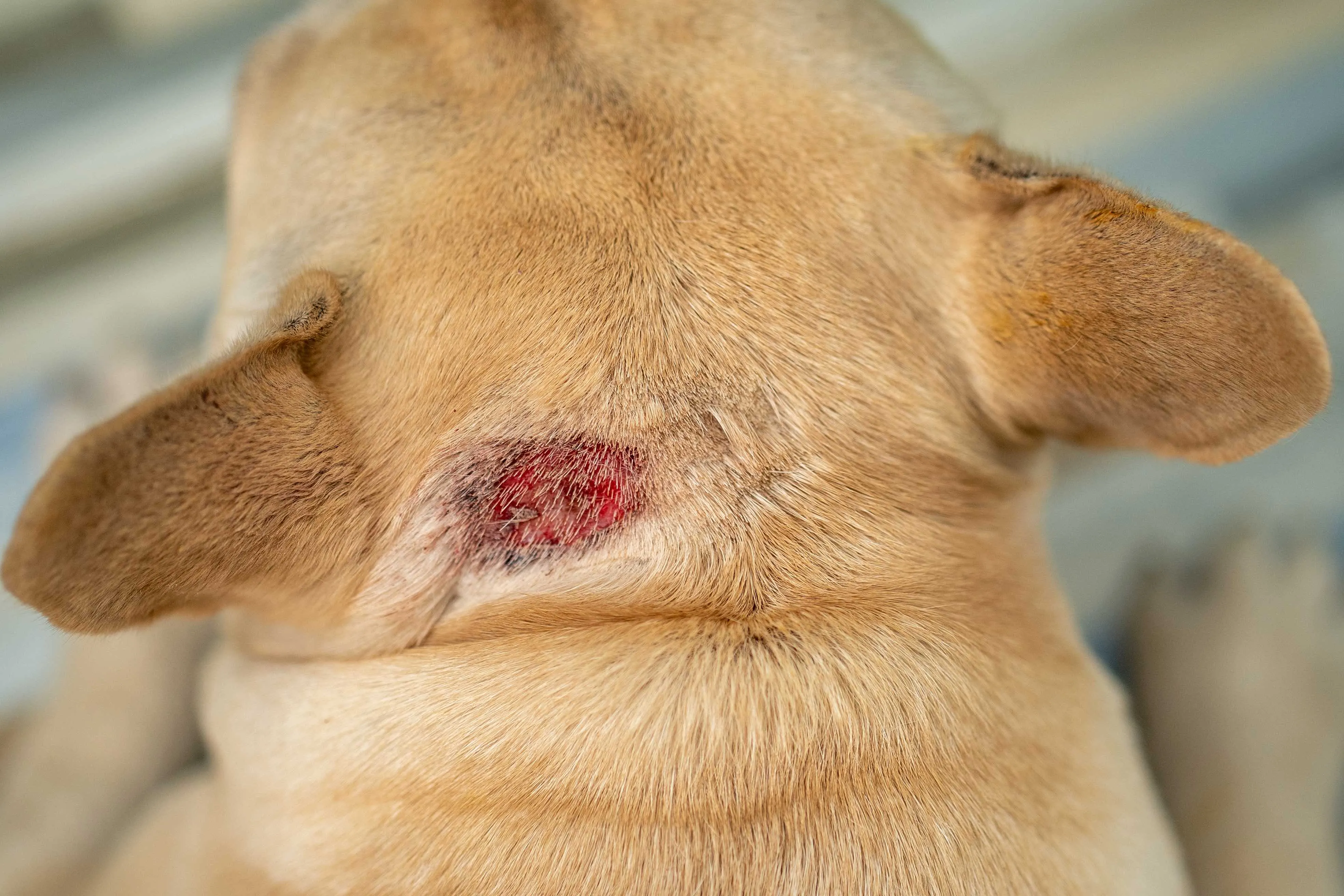 Inflamed and raw hot spot on a yellow dog's skin, demonstrating typical irritation and hair loss often seen on a dog's tail.
Inflamed and raw hot spot on a yellow dog's skin, demonstrating typical irritation and hair loss often seen on a dog's tail.
Unlike drier skin conditions such as how to heal mange on a dog or ringworm, hot spots are notably moist and inflamed. The tail can be particularly challenging to examine due to its constant motion and your dog’s discomfort, so gentle handling is essential.
Common Causes of Hot Spots on a Dog’s Tail
Hot spots on a dog’s tail are almost always triggered by an underlying issue that causes intense itching or irritation. Common culprits include:
- Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD): A single flea bite can trigger an allergic reaction, leading to severe itching, especially around the tail base, causing the dog to chew relentlessly. For comprehensive understanding of how to heal flea scabs on dogs, flea control is paramount.
- Other Allergies: Food or environmental allergies (like pollen or dust mites) can manifest as generalized itchiness, which dogs may direct towards their tail.
- Excessive Moisture: If your dog swims frequently or gets wet, and their tail doesn’t dry thoroughly, the trapped moisture can create a perfect breeding ground for bacteria and yeast.
- Poor Grooming: Matted fur around the tail can trap moisture and debris, leading to skin irritation.
- Insect Bites: Bites from mosquitos, ticks, or other insects can cause localized itching that progresses into a hot spot.
- Behavioral Licking/Chewing: Boredom, anxiety, or stress can lead to compulsive licking or chewing of the tail, even without a primary irritant.
- Anal Gland Issues: Impacted or infected anal glands can cause discomfort that makes a dog lick and chew at their tail base.
- Ear Infections: Paradoxically, an ear infection can cause dogs to be generally itchy, leading them to lick their tail or other body parts excessively. Learning how to heal a dog’s ear infection can sometimes help prevent secondary skin issues.
Certain breeds like Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherds, and English Bulldogs are genetically predisposed to various skin conditions, including hot spots, due to their coat type or skin sensitivities.
When to Seek Veterinary Care for a Tail Hot Spot
While minor hot spots can sometimes be managed at home, it’s always recommended to consult a veterinarian, especially when dealing with a hot spot on your dog’s tail. The tail is a sensitive area, and self-treatment without professional guidance might delay proper healing or miss an underlying cause. You should seek veterinary attention immediately if:
- The hot spot is rapidly increasing in size.
- There is pus, a colored discharge, or a foul odor.
- The area is consistently bleeding.
- Your dog shows significant pain or lethargy.
- You cannot prevent your dog from licking, biting, or scratching the hot spot.
- The hot spot is not showing signs of improvement after 1-2 days of home care.
A vet can accurately diagnose the underlying cause and prescribe the most effective course of treatment to prevent recurrence and ensure proper healing.
Veterinary Treatment for Hot Spots on the Tail
When you take your dog to the vet for a hot spot on their tail, the treatment approach will depend on the severity and underlying cause. Typically, a veterinarian will:
- Clip the Hair: The fur around and over the hot spot will be carefully clipped to allow the skin to breathe, dry out, and facilitate cleaning. This also prevents bacteria from being trapped.
- Cleanse the Area: The hot spot will be gently cleaned with an antiseptic solution to remove discharge, bacteria, and debris.
- Medication:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics are often prescribed to combat bacterial infections, which are common with hot spots.
- Anti-inflammatory/Anti-itch medication: Steroids (oral or topical) may be given to reduce inflammation and itching, providing immediate relief.
- Topical Treatments: Medicated sprays or creams (e.g., those containing hydrocortisone or antibiotics) might be prescribed for direct application.
- E-Collar (Recovery Cone): A recovery cone is almost always recommended to prevent your dog from licking, chewing, or scratching the area, which is crucial for healing.
- Address the Underlying Cause: Your vet will work to identify and treat the root cause. This might involve:
- Flea Control: Prescribing or recommending effective flea prevention.
- Allergy Management: Discussing dietary changes, allergy medications, or immunotherapy.
- Behavioral Therapy: If excessive licking is due to anxiety, behavioral modification strategies may be suggested.
Effective Home Remedies for Healing a Dog’s Tail Hot Spot
While a vet visit is paramount, there are steps you can take at home to help manage and soothe a hot spot on your dog’s tail, especially before your vet appointment.
Important Note: NEVER use human medications like Neosporin®, hydrocortisone creams, or Vaseline® on your dog’s hot spot. Dogs tend to lick off topical ointments, which can be harmful if ingested and hinder healing by keeping the area moist.
Follow these steps for home care:
- Trim the Area: Carefully use dog hair clippers (never scissors, to avoid accidental cuts) to trim the fur around the hot spot. This exposes the lesion to air, prevents moisture retention, and allows you to clean it effectively.
- Cleanse Gently: Using a mild, water-based antiseptic spray or wipe designed for pets, such as a chlorhexidine-based solution, gently clean the hot spot. This helps remove bacteria and keeps the area clean.
- Apply Pet-Safe Spray: Apply a veterinary-recommended hot spot spray that is safe if ingested. Products like Vetericyn® Plus Antimicrobial Pet Hot Spot Spray can help with healing and provide comfort.
- Prevent Licking: It is absolutely critical to prevent your dog from licking, chewing, or scratching the hot spot. Use a recovery cone (E-collar) immediately. Consistent use of the cone is key for the hot spot to heal.
- Monitor Progress: Observe the hot spot daily for signs of improvement, such as decreased redness, less moisture, and a reduction in size. If the condition worsens or doesn’t improve within 24-48 hours, contact your veterinarian.
Preventing Recurrent Hot Spots on Your Dog’s Tail
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to hot spots on a dog’s tail. By addressing the common underlying causes, you can significantly reduce the risk of future occurrences:
- Consistent Flea and Tick Prevention: Maintain a strict year-round flea and tick control regimen recommended by your vet.
- Regular Grooming: Brush your dog’s coat regularly, paying extra attention to the tail area, to prevent matting. If your dog has a thick coat, professional grooming can help.
- Thorough Drying: After baths or swimming, ensure your dog’s tail and the fur around it are completely dry.
- Allergy Management: Work with your vet to identify and manage any underlying food or environmental allergies. This may involve special diets, medications, or allergy shots.
- Address Boredom and Anxiety: Provide plenty of physical exercise and mental stimulation through interactive toys or training to prevent compulsive licking behaviors stemming from boredom or stress.
- Routine Vet Check-ups: Regular veterinary visits can help detect and address issues like anal gland problems or ear infections before they lead to hot spots. Timely management of issues like how to heal pressure sores on dogs or other dermatological concerns can contribute to overall skin health.
Conclusion
Hot spots on a dog’s tail can be painful and frustrating for both pets and their owners. By understanding what hot spots are, their common causes, and implementing a combination of veterinary care and diligent home management, you can effectively treat and prevent these recurring skin irritations. Early detection, prompt action, and a commitment to addressing the root cause are your best strategies for ensuring your dog’s tail remains healthy and itch-free. Always consult with your veterinarian for personalized advice and the most appropriate treatment plan for your beloved canine companion.
