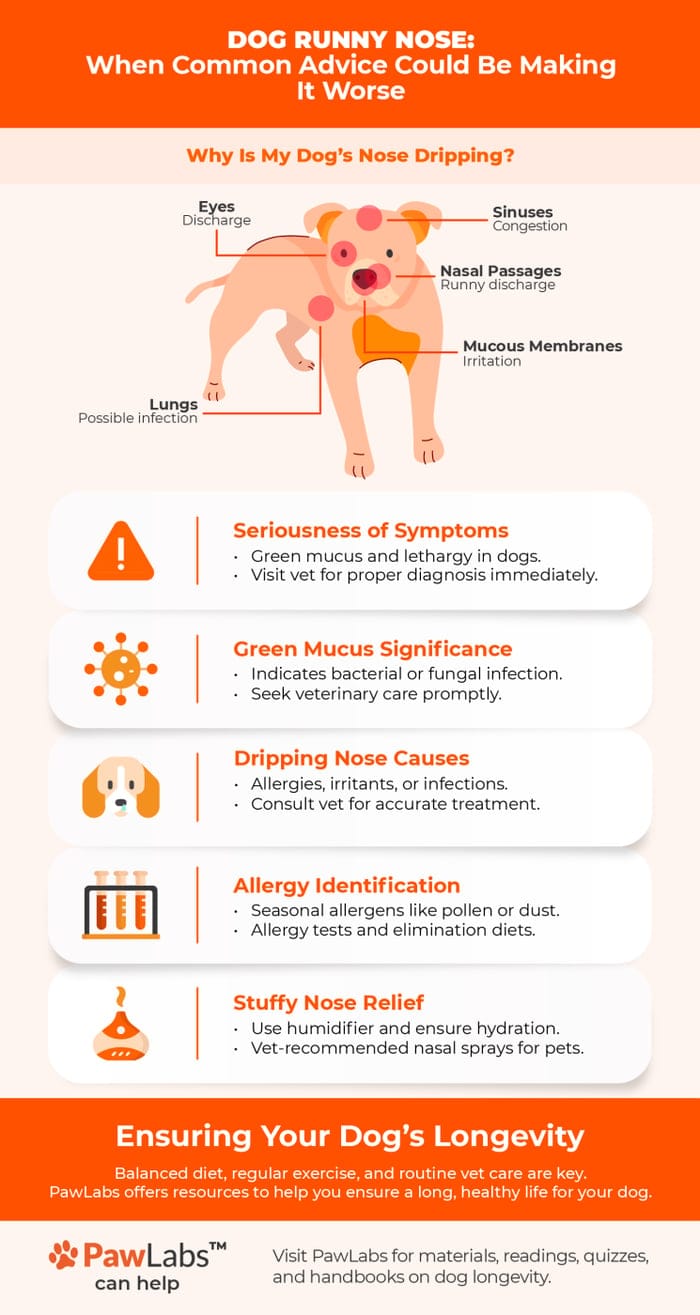
Nasal discharge in dogs can range from a minor inconvenience to a sign of a serious health issue. Understanding the potential causes and appropriate treatments is crucial for any dog owner. This guide will explore common reasons for nasal discharge, from infections and growths to structural problems and diseases, and outline the veterinary approaches to address them.
Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacterial infections in a dog’s nasal passages often require a course of antibiotics prescribed by a veterinarian. Treatment can sometimes last for several weeks to effectively clear the infection. Similarly, fungal infections necessitate specific antifungal medications to combat the growth. In cases of chronic or persistent infections, surgical intervention might be recommended by your vet.
Nasal Polyps and Tumors
Overgrown mucus-producing glands, known as nasal polyps, or nasal tumors can lead to discharge that may contain blood, pus, or mucus. Other symptoms might include noisy breathing, a visible bulge on the side of the nose, and a decreased appetite.
Surgery is the primary treatment for nasal polyps, although they have a tendency to recur, potentially requiring further treatment. For nasal tumors, treatment options vary. Benign tumors can often be surgically removed. However, cancerous nasal tumors are typically managed with radiation therapy, as surgical removal is rarely successful, and the prognosis for these cases is generally poor.
Nostril Problems
Certain breeds, particularly those with flat faces (brachycephalic breeds) or soft, floppy nose cartilage, may be more predisposed to nasal discharge and noisy breathing. These conditions can be related to the physical structure of their nostrils.
In some instances, surgery may be necessary to correct small nostrils or address cartilage issues. This type of surgery is often postponed until the dog has reached adulthood.
Distemper
Canine distemper is a serious viral illness that can cause a sticky, yellow nasal discharge. The symptoms of distemper can vary widely but may also include fever, pneumonia, twitching, and convulsions.
Treatment for distemper is symptomatic and can involve a combination of anticonvulsants, antibiotics, sedatives, and painkillers. Prevention is key, and puppies should receive a series of vaccinations, typically starting at a young age and completing around 16 weeks. Adult dogs also require regular booster shots according to their veterinarian’s recommended schedule. Breeding females should be vaccinated several weeks before mating to protect their offspring.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
This bacterial disease, transmitted by infected ticks, can manifest as nosebleeds in dogs. Other signs include high fever, lethargy, coughing, and inflammation of the eyes, along with general pain.
Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics lasting several weeks. To prevent this potentially serious disease, it’s essential to use tick prevention products and minimize your dog’s exposure to ticks.
Cleft Palate or Fistula
If your dog experiences nasal discharge after eating, it could indicate a cleft palate, a condition where the palate doesn’t fuse properly, or an oral-nasal fistula, which is a hole connecting the mouth and nasal cavity. These fistulas can result from issues like severe tooth decay, injury, infection, or previous surgery.
Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for both cleft palates and oral-nasal fistulas.
References
- WebMD. (n.d.). Bacterial infections. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/bacterial-and-viral-infections
- WebMD. (n.d.). Antibiotics. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/cold-and-flu/cm/rm-quiz-antibiotics-myths-facts
- WebMD. (n.d.). Nasal polyps symptoms and treatments. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/allergies/nasal-polyps-symptoms-and-treatments
- WebMD. (n.d.). Benign tumors. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/benign-tumors-causes-treatments
- WebMD. (n.d.). What to Expect From Radiation Therapy. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/cancer/what-to-expect-from-radiation-therapy
- WebMD. (n.d.). Tic Disorders and Twitches. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/brain/tic-disorders-and-twitches
- WebMD. (n.d.). Nighttime Cough. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/cold-and-flu/cm/rm-quiz-nighttime-cough
- WebMD. (n.d.). About Inflammation. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/about-inflammation
- WebMD. (n.d.). Picture of the Eyes. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/picture-of-the-eyes
- WebMD. (n.d.). Fevers: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/fevers-causes-symptoms-treatments
- WebMD. (n.d.). Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/cleft-lip-cleft-palate
- WebMD. (n.d.). Teeth and Gum Care. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/teeth-and-gum-care