Your dog’s skin is their largest organ, playing a crucial role in their overall health and well-being. However, skin conditions are among the most frequent reasons for veterinary visits. Recognizing common dog skin problems can help you identify potential issues and seek timely treatment. Learn more about CECS syndrome in dogs to understand a specific, though less common, condition.
Identifying Symptoms of Skin Problems in Dogs
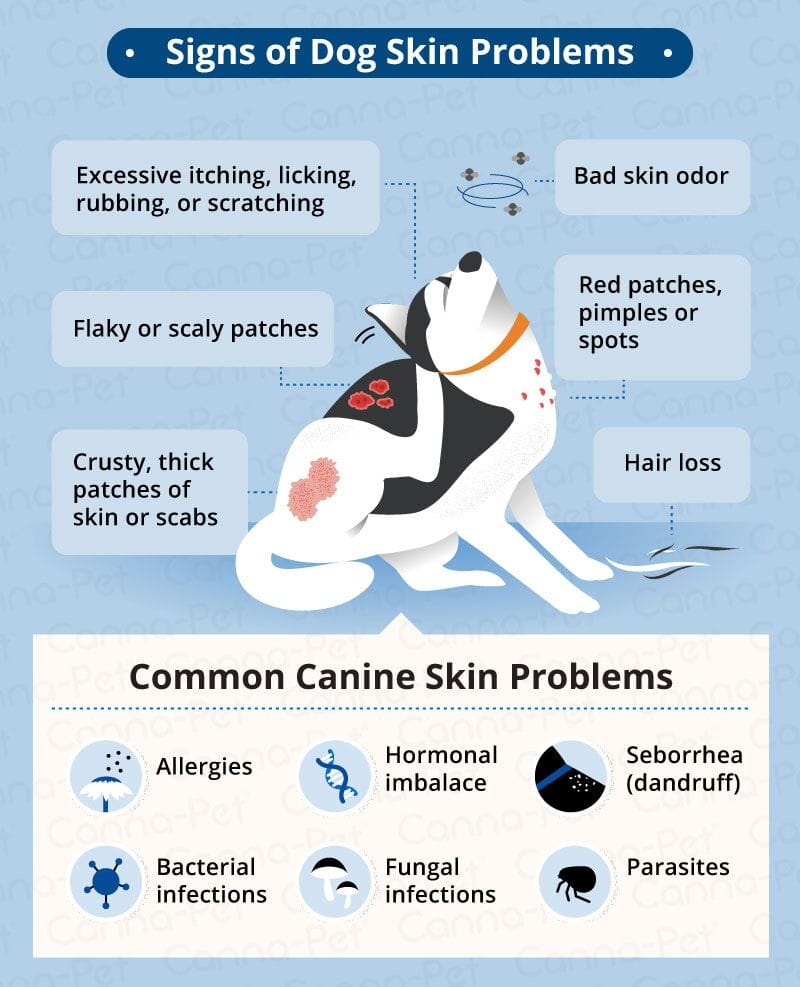
Healthy canine skin should feel soft and appear clear, free from bumps, scales, or discoloration. If your dog is experiencing a skin issue, you might observe several common symptoms:
- Scales or flakes: Indicating dryness or underlying irritation.
- Redness: Suggesting inflammation or infection.
- Hair loss: Can be a sign of allergies, parasites, or other health issues.
- Discoloration: Changes in skin pigmentation may point to chronic irritation or disease.
- Odor: A persistent, unpleasant smell can signal infection.
- Itching: Excessive scratching, licking, or chewing is a hallmark of many skin problems.
- Greasiness: An oily coat might indicate hormonal imbalances or overactive sebaceous glands.
- Scabbing: Often a result of scratching or skin infections.
- Bumps: Can range from mild irritation to more serious growths.
- Oozing sores: May indicate infection or a more severe inflammatory process.
Top 10 Dog Skin Disorders
1. Allergies
Allergies are a prevalent cause of skin issues in dogs. They can be triggered by various factors, including fleas, specific food ingredients, or environmental allergens like pollen, dust, and mold. Many dogs react to a combination of these. When exposed to an allergen, a dog’s body releases histamine, leading to intense itching. Management often involves allergy medications or strict avoidance of the offending allergen.
2. Parasites
External parasites are a frequent culprit behind canine skin problems. The most common offenders include fleas, ticks, and mites. Fortunately, preventative measures using high-quality products can significantly reduce the risk of infestation. Brands like NexGard, Bravecto, Credelio, and Revolution offer effective protection.
Fleas are prolific egg-layers, and even a single flea can infest an environment quickly. You might notice adult fleas or “flea dirt” (fecal matter) in your dog’s fur. Some dogs develop severe allergic reactions to flea bites, resulting in intense itching and hair loss.
Ticks can remain attached to a dog for days, feeding on their blood. Prompt and proper removal of any discovered ticks is crucial to prevent the transmission of diseases. If you find a tick, remove it carefully, ensuring the entire tick, including its head, is extracted.
Commonly diagnosed mites in dogs include:
- Sarcoptes: Highly contagious, causing significant itching and hair loss.
- Demodex: Normally present on the skin, but can overgrow in immunocompromised dogs, leading to hair loss, particularly around the eyes and paws.
- Cheyletiella: Often referred to as “walking dandruff,” these mites appear as small white flakes and may or may not cause itching.
3. Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial infections are a common skin disorder in dogs, frequently stemming from an overgrowth of naturally occurring skin bacteria. This overgrowth often occurs when a dog’s immune system is compromised by other conditions, such as allergies. Signs include red, scaly patches, small red bumps or pustules, and moist, inflamed areas. Infections can also arise when foreign bacteria enter the skin through minor abrasions. Treatment typically involves oral antibiotics or the use of medicated shampoos, such as KetoChlor® or Douxo®.
4. Hot Spots
Hot spots are acutely inflamed, moist, red patches of skin that can appear suddenly. They are typically a result of an underlying allergy that causes intense itching. Dogs may incessantly rub, scratch, lick, or chew at an affected area, creating a hairless wound that becomes hot, sensitive, and painful. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and anti-itch medications. Over-the-counter sprays like Vetericyn® Plus Antimicrobial may also be recommended for relief.
5. Yeast Infections
Yeast skin infections are caused by an overgrowth of yeast organisms on the skin, leading to a characteristic musky odor and persistent itching. Chronic yeast infections can cause hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin), particularly in the belly, groin, and armpit areas. You might also notice black debris at the nail beds. Antifungal medications, either oral or topical, are the standard treatment.
6. Ringworm
Despite its name, ringworm is a fungal infection, not caused by a worm. In dogs, it typically manifests as localized patches of hair loss and scaly skin, which can be itchy. Because ringworm is zoonotic, it can be transmitted to humans. Treatment involves topical and oral antifungal medications.
7. Dry Skin
Dry skin in dogs, often accompanied by flakiness (dander), can have numerous causes. While it can be a normal puppy condition as oil glands develop, dry weather is also a common factor. In some cases, it may signal inadequate nutrition or an underlying health issue. Treatments can include moisturizing leave-on products or oral omega-3 fatty acid skin supplements.
8. Alopecia
Alopecia, or hair loss, can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, including allergies, parasites, adverse drug reactions, skin infections, genetic predispositions, hypothyroidism, and Cushing’s disease. If hair loss occurs without obvious signs of infection or parasites, your veterinarian may recommend diagnostic blood work to check for systemic diseases.
A specific type, known as alopecia X, is a genetic condition more common in breeds with thick undercoats like Pomeranians, Chow Chows, and Alaskan Malamutes. Affected dogs lose hair without skin inflammation. Neutering male dogs may improve alopecia X, and melatonin can sometimes be beneficial.
9. Skin Cancer
Skin cancer in dogs can manifest as hair loss, scabs, oozing lesions, or lumps and bumps. Some forms present as obvious masses, while others may cause more subtle changes. Any persistent non-healing wounds or discolored skin patches warrant examination by a veterinarian. Diagnosis is often confirmed through a biopsy, and treatment may include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
10. Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune diseases occur when a dog’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own body tissues. These conditions are often inherited but can sometimes be triggered by medications. Common examples include pemphigus and lupus, which can cause crusting lesions and hair loss, particularly along the bridge of the nose and on the face. Treatment typically involves immunosuppressive medications like prednisone or cyclosporine, tailored to the specific disease. Avoiding excessive sun exposure may also be recommended.
Dr. Melissa Boldan, DVM, contributed to this article. She graduated from the University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine in 2012 and has extensive experience in veterinary practice.