Choosing the right food for your puppy is a critical decision that impacts their growth, health, and overall well-being. This guide delves into the essential components of a high-quality puppy food, focusing on the nutritional needs of growing dogs and offering insights for pet owners to make informed choices. Understanding the ingredients, guaranteed analysis, and feeding guidelines will empower you to provide the best start for your furry companion.
Understanding Puppy Food Ingredients
A well-formulated puppy food is built upon a foundation of quality ingredients that provide essential nutrients for rapid development.
Key Protein Sources
High-quality puppy foods typically feature named meat meals or fresh meats as primary ingredients. Chicken by-product meal, a concentrated source of protein and essential amino acids, is a common and beneficial ingredient, also providing glucosamine for joint health. Whole grains like corn and wheat flour offer carbohydrates for energy and fiber for digestive health.
Healthy Fats and Oils
Chicken fat is a valuable source of omega-6 fatty acids, crucial for skin and coat health, as well as energy. Fish meal and salmon oil are important for their omega-3 fatty acid content, particularly DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid), which plays a vital role in brain and vision development. Flaxseed also contributes to a healthy fatty acid profile.
Vitamins, Minerals, and Probiotics
A comprehensive vitamin and mineral premix ensures that puppies receive all the micronutrients necessary for growth. This includes essential vitamins like A and E, minerals like zinc and selenium, and specific amino acids like methionine. The inclusion of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Enterococcus faecium, and Bifidobacterium animalis, supports a healthy digestive system and immune function by introducing beneficial microorganisms.
Guaranteed Analysis: Decoding Nutritional Content
The guaranteed analysis on a puppy food label provides a snapshot of the minimum and maximum percentages of key nutrients.
Macronutrients
- Crude Protein: A minimum of 31.0% is essential for muscle development and overall growth.
- Crude Fat: A minimum of 20.0% provides energy and supports nutrient absorption.
- Crude Fiber: A maximum of 3.0% indicates the amount of indigestible material, important for digestive regularity.
- Moisture: A maximum of 10.0% ensures the food is shelf-stable and nutrient-dense.
Essential Fatty Acids and Minerals
- Methionine: A minimum of 0.6% is a crucial amino acid for protein synthesis and growth.
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): A minimum of 0.05% is vital for cognitive and visual development.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Minimum levels of 1.2% and 1.0%, respectively, are critical for strong bone and teeth formation, and must be in the correct ratio.
- Zinc and Selenium: Minimum levels of 200 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg, respectively, are important for immune function and metabolic processes.
- Vitamin A and Vitamin E: Minimum levels of 10,000 IU/kg and 150 IU/kg, respectively, support vision, immune health, and act as antioxidants.
Specialized Nutrients
- Glucosamine: A minimum of 500 mg/kg supports joint health, particularly important for large breed puppies.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: A minimum of 3.3% and Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A minimum of 0.5% contribute to healthy skin, a shiny coat, and reduced inflammation.
- Total Microorganisms: A minimum of 80,000,000 CFU/lb ensures a robust population of beneficial bacteria for gut health.
It’s important to note that some nutrients, like Glucosamine and certain fatty acids, may not be recognized as essential by AAFCO but still offer significant health benefits.
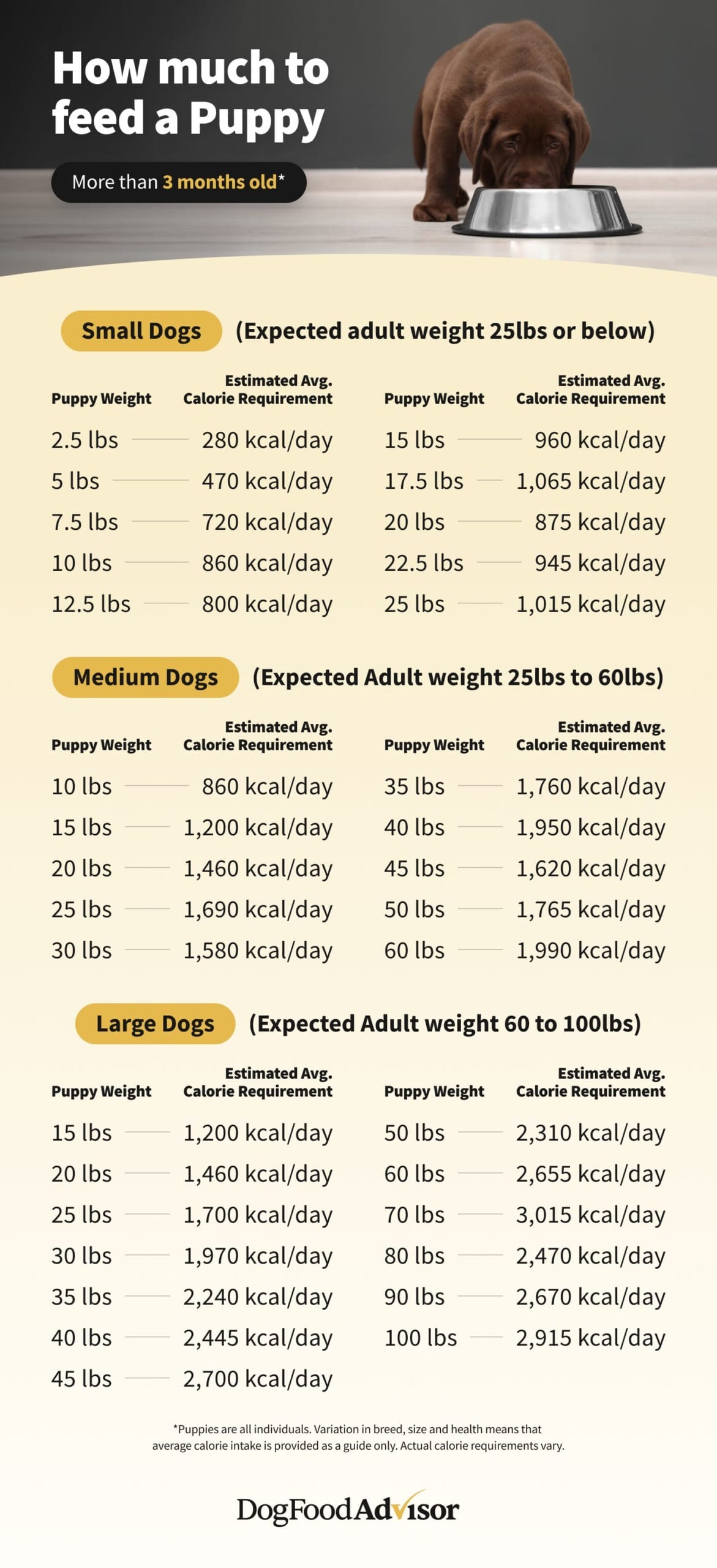
Feeding Guidelines for Growing Puppies
Establishing appropriate feeding practices is key to ensuring your puppy reaches a healthy adult weight and avoids common health issues like obesity.
Determining Portion Sizes
The feeding chart provides a starting point based on your puppy’s current weight and age. For example, a 3-5 lb puppy between 2-4 months of age would typically consume between ⅔ and ¾ cup of food per day. As puppies grow, their caloric needs change, and portion sizes should be adjusted accordingly.
Adjusting for Life Stages and Conditions
- Older Puppies: As puppies transition through different age brackets (4-8 months, 8-12 months), their food intake may slightly decrease as their growth rate slows.
- Adult Dogs: Adult dogs of similar weights require less food than puppies, with portion sizes decreasing significantly.
- Large Breed Puppies: For adult dogs over 100 pounds, an additional ⅓ cup of food is recommended for every 10 pounds of body weight.
- Pregnant or Nursing Dogs: These dogs have significantly increased energy demands and are often recommended for free-choice feeding to meet their nutritional needs.
Monitoring and Veterinary Consultation
The most crucial aspect of feeding is monitoring your puppy’s body condition. Adjustments should be made to the daily amount offered to maintain an ideal body condition, preventing both undernourishment and overfeeding. Because individual needs vary based on activity level, metabolism, and genetics, consulting with your veterinarian is paramount. They can help determine your dog’s ideal adult weight and provide personalized feeding recommendations.
Hydration is Key
Always ensure that fresh, clean water is readily available to your puppy at all times. Proper hydration is fundamental to all bodily functions and overall health.
This high-quality puppy food is formulated to meet the nutritional levels established by the AAFCO Dog Food Nutrient Profiles for All Life Stages, including the growth of large-size dogs. It is available in various sizes, from 6oz to 40lb bags, catering to different needs and household sizes.
References:
- Ingredient list and Guaranteed Analysis provided in the original text.
- Feeding guidelines and recommendations provided in the original text.